Contact tracing with Ebola
Quantifying the impact of early-stage contact tracing using activity driven networks
Contact tracing is a mitigation strategy which can help contain an infectious outbreak if it is deployed in time. In this work, we use analyze the effect of early-stage contact tracing using a mathematical modeling framework. We use a patient-centric dynamic contact model using activity driven networks (ADN). To simulate the disease spread and the contact tracing process, we use a stochastic transitions among epidemiological states
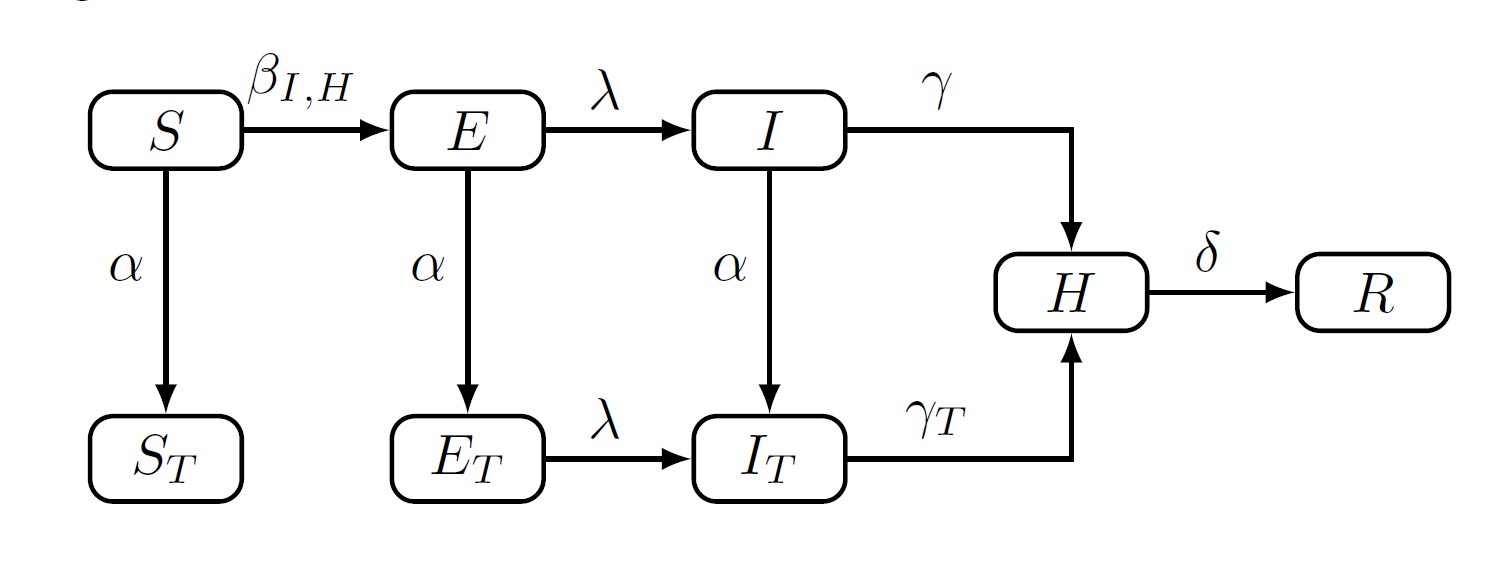
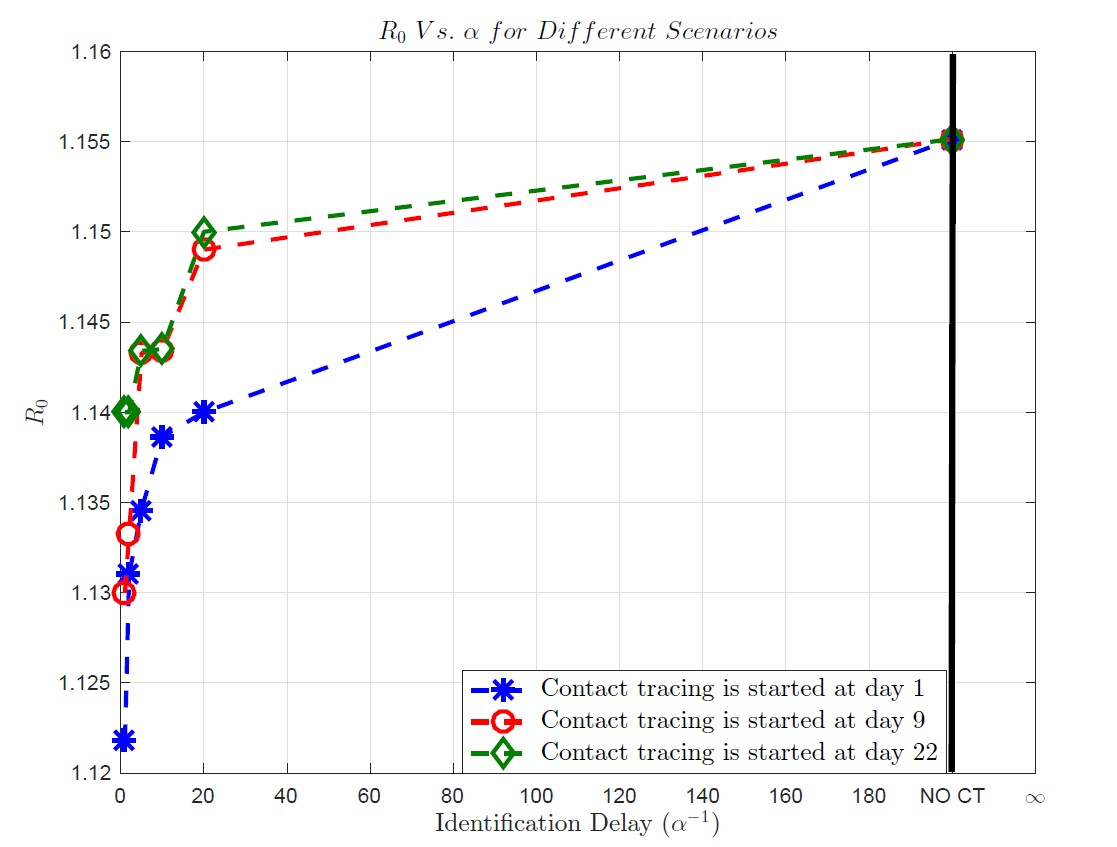
Our results indicate that it is critical to start contact tracing within a few days (< 10 days), if not immediately after the disease emergence. Quick identification of contacts can reduce the outbreak size up to 50% compared to delayed detection.
| Publication | Source Code | Official Project Page |
|---|---|---|
| Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering | Not Published | K-State NetSE |